ELK
简介
ELK 是 Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana 的简称,它们都是开源软件,通常一起使用来收集、存储、搜索和分析数据。
- Elasticsearch:一个分布式搜索和分析引擎,用于存储和搜索大量数据。它提供了全文搜索、结构化搜索、分析等功能。
- Logstash:一个数据处理管道,用于收集、处理和转发日志和事件数据。它可以从各种来源收集数据,并进行格式转换、过滤、解析等操作。然后将数据发送到 Elasticsearch。
- Kibana:一个数据可视化工具,用于创建仪表板和可视化数据。它可以与 Elasticsearch 集成,提供丰富的数据可视化功能,帮助用户更好地理解数据。
- Beats:轻量级的数据收集器,用于将数据发送到 Logstash 或 Elasticsearch。Beats 包括 Filebeat(用于收集日志文件)、Metricbeat(用于收集系统和服务指标)等。

ElasticSearch
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式搜索和分析引擎,用于存储和搜索大量数据。它提供了全文搜索、结构化搜索、分析等功能。Elasticsearch 使用 JSON 格式存储数据,并使用倒排索引来加速搜索。所谓倒排索引,就是将文档中的每个词映射到包含该词的文档列表,通过查询关键词,可以快速找到包含该关键词的文档。
数据格式
- index:索引,类似于数据库中的数据库。
- type:类型,类似于数据库中的表。
- document:文档,类似于数据库中的行。
- field:字段,类似于数据库中的列。
数据库操作
- 查询所有索引数据: GET /_cat/indices?v
PUT http://localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v
Response:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open shopping EUd-Fh97S8WkTG5VIkV6TA 1 0 0 0 225b 225b- 创建索引:PUT /index_name
PUT http://localhost:9200/shopping
Response:
{
"acknowledged": true,
"shards_acknowledged": true,
"index": "sleep"
}- 删除索引:DELETE /index_name
DELETE http://localhost:9200/shopping
Response:
{
"acknowledged": true
}- 查询索引:GET /index_name
GET http://localhost:9200/shopping
Response:
{
"shopping": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "shopping",
"creation_date": "1753983017737",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "EUd-Fh97S8WkTG5VIkV6TA",
"version": {
"created": "9009000"
}
}
}
}
}- 插入更新文档:PUT、POST /index_name/_doc/{id},请求体为 JSON 格式的数据,uri中必须要有$_doc$
POST http://localhost:9200/shopping/_doc/1
Content-Type: application/json
{
"title": "Macbook Pro",
"price": 2000,
"description": "Macbook Pro 16 inch"
}
Response:
{
"_index": "shopping",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"result": "created",
"_shards": {
},
"_seq_no": 1,
"_primary_term": 1
}- 部分更新文档:POST /index_name/_update/{id},请求体为 JSON 格式的数据,一定要有$doc$
POST http://localhost:9200/shopping/_update/1
Content-Type: application/json
{
"doc": {
"title": "Macbook Pro 1",
"price": 2000,
"description": "Macbook Pro 16 inch"
}
}PUT为幂等操作,POST为非幂等操作,PUT会覆盖原有数据,使用时必须指定id,POST会自动生成id,不需要指定id,如果指定id那就是更新。PUT为全量更新替换,POST通过_update进行部分更新。
查询操作:GET /index_name/_doc/{id}
GET http://localhost:9200/shopping/_search
Content-type: application/json
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "MacBook"
}
},
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
],
"_source": ["title", "price"],
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
###
GET http://localhost:9200/shopping/_search
Content-type: application/json
{
"aggs":{ # 聚合查询
"price_group":{ # 查询名称随意即可
"terms":{ # 聚合类型-分组
"field": "price" # 聚合字段
}
}
},
"size":0 # 不返回数据
}核心API总结
| 操作 | 方法 | 端点 | 文档 ID 来源 | 结果 (ID 不存在) | 结果 (ID 存在) | 主要用途 | 更新类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 创建 (自动 ID) | POST |
/<index>/_doc |
ES 自动生成 | 创建 新文档 | (不适用 - 总是新 ID) | 新增日志事件、未知 ID 的数据导入 | - |
| 创建或全量替换 | PUT |
/<index>/_doc/<id> |
用户明确指定 | 创建 新文档 | 替换 整个现有文档 | 提供完整 ID 时的索引、强制覆盖旧文档版本 | 全量替换 |
| 强制创建 (仅当不存在) | PUT/POST |
/<index>/_create/<id> |
用户明确指定 | 创建 新文档 | 失败 (409 Conflict) | 确保不覆盖的初始化、“仅当不存在时”操作 | - |
| 部分更新 | POST |
/<index>/_update/<id> |
用户明确指定 | 失败 (404 Not Found) | 更新 指定字段 | 修改文档的特定部分(如计数器、状态标记、描述) | 部分更新 |
文档操作类:
关键词 作用 示例 _doc基础文档操作端点(GET查询,PUT/POST创建文档) PUT /index/_doc/1_create强制创建(仅当ID不存在) PUT /index/_create/1_update部分更新文档 POST /index/_update/1_bulk批量操作API POST /_bulk_source获取文档原始内容 GET /index/_source/1_mget批量获取多文档 GET /index/_mget索引管理类:
关键词 作用 示例 _mapping管理字段映射 PUT /index/_mapping_settings管理索引配置 PUT /index/_settings_alias操作索引别名 POST /_aliases_forcemerge强制合并段文件 POST /index/_forcemerge搜索查询类:
关键词 作用 示例 _search执行搜索请求 GET /index/_search_count统计匹配文档数 GET /index/_count_explain解释文档相关性评分 GET /index/_explain/1_knn_search向量相似度搜索 (8.0+) POST /index/_knn_search集群监控类:
关键词 作用 示例 _cat监控命令入口 (含60+子端点) GET /_cat/indices_cluster集群操作 GET /_cluster/health_nodes节点管理 GET /_nodes/stats_tasks管理异步任务 GET /_tasks?detailed=true安全类(这个在原回答中只有两列,没有示例列):
关键词 作用 _security用户/角色权限管理 _api_keyAPI密钥管理 _oidcOpenID Connect认证
代码实战
- 依赖引入
<!-- 高级客户端,es8+之后推荐 -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/co.elastic.clients/elasticsearch-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>co.elastic.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-java</artifactId>
<version>9.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 高级客户端,不过只适用于es7+ -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.elasticsearch.client/elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
<version>7.17.29</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 低级客户端,基础的线程管理和http访问 -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.elasticsearch.client/elasticsearch-rest-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-client</artifactId>
<version>9.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 如果使用springboot项目,使用此依赖可以通过spring进行管理,通过注解简化开发 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>4.4.18</version>
</dependency>- 代码示例
package com.example.es;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchClient;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch._types.Refresh;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch._types.SortOptions;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch._types.SortOrder;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.*;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.core.search.Hit;
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.indices.CreateIndexResponse;
import co.elastic.clients.json.jackson.JacksonJsonpMapper;
import co.elastic.clients.transport.rest_client.RestClientTransport;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
class EsApplicationTests {
static class Product {
public String id;
public String name;
public double price;
public String category;
Product() {
}
public Product(String id, String name, double price, String category) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.category = category;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(String category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
public static ElasticsearchClient client;
@Test
public void testEs() throws Exception {
RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("localhost", 9200, "http")
).build();
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());
RestClientTransport restClientTransport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper(objectMapper));
client = new ElasticsearchClient(restClientTransport);
createProductIndex();
Product product = new Product("p1", "Laptop", 1299.99, "Electronics");
indexProduct(product); // 创建文
getProduct("p1"); // 获取文档
updateProductPrice("p1", 1199.99); // 更新文档
searchProducts("Laptop"); // 搜索文档
searchAllProducts();
deleteProduct("p1"); // 删除文档档
restClient.close();
}
// ========= 索引操作 =========
private static void createProductIndex() throws IOException {
// 检查索引是否存在
boolean exists = client.indices()
.exists(e -> e.index("products"))
.value();
if (!exists) {
// 创建索引并配置映射
CreateIndexResponse response = client.indices().create(c -> c
.index("products")
.mappings(m -> m
.properties("id", p -> p.keyword(k -> k))
.properties("name", p -> p.text(k -> k))
.properties("price", p -> p.text(k -> k))
.properties("category", p -> p.text(k -> k))
)
);
System.out.println("索引创建结果: " + response.acknowledged());
}
}
// ========= 文档操作 =========
// 1. 索引文档 (UPSERT)
private static void indexProduct(Product product) throws IOException {
IndexResponse response = client.index(i -> i
.index("products")
.id(product.getId())
.document(product)
);
System.out.println("索引文档结果: " + response.result());
}
// 2. 获取文档
private static void getProduct(String id) throws IOException {
GetResponse<Product> response = client.get(g -> g
.index("products")
.id(id),
Product.class
);
if (response.found()) {
Product product = response.source();
System.out.println("获取到的产品: " + product.getName() + ", 价格: $" + product.getPrice());
} else {
System.out.println("文档不存在");
}
}
// 3. 更新文档 (部分更新)
private static void updateProductPrice(String id, double newPrice) throws IOException {
Map<String, Object> updatefield = new HashMap<>();
updatefield.put("price", newPrice);
UpdateResponse<Product> response = client.update(u -> u
.index("products")
.id(id)
.doc(updatefield)
.refresh(Refresh.True),
Product.class
);
System.out.println("更新结果: " + response.result());
}
// 4. 搜索文档
private static void searchProducts(String keyword) throws IOException {
SearchResponse<Product> response = client.search(s -> s
.index("products")
.query(q -> q
.match(m -> m
.field("name")
.query(keyword)
)
)
.from(0)
.size(10)
.sort(SortOptions.of(so -> so
.field(f -> f
.field("price")
.order(SortOrder.Desc)
)
)
)
.source(sc -> sc
.filter( f->f
.excludes("price")
.includes("name"))
),
Product.class
);
System.out.println("====== 搜索结果 =====");
System.out.println("总命中数: " + response.hits().total().value());
for (Hit<Product> hit : response.hits().hits()) {
Product p = hit.source();
System.out.printf("[%s] %s - $%.2f\n",
p.getId(), p.getName(), p.getPrice());
}
}
// 5. 删除文档
private static void deleteProduct(String id) throws IOException {
DeleteResponse response = client.delete(d -> d
.index("products")
.id(id)
);
System.out.println("删除结果: " + response.result());
}
// 6. 搜索文档
private static void searchAllProducts() throws IOException {
SearchResponse<Product> response = client.search(s -> s
.index("products")
.query(q -> q
.matchAll(m -> m)
),
Product.class
);
System.out.println("====== 全量查询结果 =====");
System.out.println("总命中数: " + response.hits().total().value());
for (Hit<Product> hit : response.hits().hits()) {
Product p = hit.source();
System.out.printf("[%s] %s - $%.2f\n",
p.getId(), p.getName(), p.getPrice());
}
}
}
- springboot集成elasticsearch
import co.elastic.clients.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchClient;
import co.elastic.clients.json.jackson.JacksonJsonpMapper;
import co.elastic.clients.transport.ElasticsearchTransport;
import co.elastic.clients.transport.rest_client.RestClientTransport;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.client.elc.ElasticsearchTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchOperations;
@Configuration
public class ElasticsearchConfig {
@Value("${elasticsearch.host:localhost}")
private String host;
@Value("${elasticsearch.port:9200}")
private int port;
@Bean
public ElasticsearchClient elasticsearchClient() {
// 1. 创建底层REST客户端
RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost(host, port, "http")
).build();
// 2. 创建JSON映射器
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.registerModule(new JavaTimeModule()); // 支持Java时间类型
// 3. 创建传输层
ElasticsearchTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(
restClient,
new JacksonJsonpMapper(mapper)
);
// 4. 创建客户端实例
return new ElasticsearchClient(transport);
}
// 可选:Spring Data Repository支持
@Bean
public ElasticsearchOperations elasticsearchTemplate(ElasticsearchClient restClient) {
return new ElasticsearchTemplate(restClient);
}
}package com.example.es;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Document(indexName = "product")
public class Product {
@Id
private Long id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String category;
@Field(type = FieldType.Double)
private Double price;
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword,index = false)
private String images;
}
public interface ProductRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Product, String> {
// 自动实现查询方法
List<Product> findByName(String name);
// 自定义查询
@Query("{\"match\": {\"name\": \"?0\"}}")
Page<Product> findByNameCustom(String name, Pageable pageable);
// 聚合查询
@Aggregation(pipeline = {
"{'$group': {'_id': '$category', 'avgPrice': {'$avg': '$price'}}}"
})
Aggregations<Product> averagePriceByCategory();
}Product product = new Product("p1", "Laptop", 1299.99);
IndexQuery indexQuery = new IndexQueryBuilder()
.withId(product.getId())
.withObject(product)
.build();
String documentId = elasticsearchOperations.index(indexQuery, IndexCoordinates.of("products"));
集群
- 配置文件
# 同一个集群的所有节点必须使用相同的 cluster.name
cluster.name: my-cluster
# 节点名称,不同的节点不同
node.name: node-1
# 节点角色
node.master: true
# 存储数据
node.data: true
# 节点角色
node.roles:
- data
- ingest
- ml
# 数据目录
path.data: /path/to/data
# 日志目录
path.logs: /path/to/logs
# 网络绑定地址
network.host: localhost
# 端口
http.port: 9201
# tpc节点之间通信端口
transport.tcp.port: 9301
# 跨域访问
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
# 集群发现
#用于指定集群自动发现所需的初始主机节点列表(不要求一定是主节点)。这些主机节点用于引导新加入的节点发现和加入集群。
discovery.seed_hosts: [“192.168.25.31:9300”, “192.168.25.32:9300”, “192.168.25.33:9300”]
#用于指定集群的初始主节点列表。这些节点在集群启动时负责选举出主节点,并承担集群的管理和协调工作。
cluster.initial_master_nodes: [“node-1”, “node-2”, “node-3”]
discovery.zen.fd.ping_timeout: 1m
discovery.zen.fd.ping_interval: 30s
discovery.zen.fd.ping_retries: 5
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 1
- 创建节点时指定分片数和副本数
// 创建索引时指定分片数和副本数
CreateIndexResponse createIndexResponse = client.indices().create(c -> c
.index("my-index")
.settings(s -> s
.numberOfShards(3)
.numberOfReplicas(2)
)
);- 数据新增时,路由计算:根据文档的_id进行哈希,然后对分片数取模,得到该文档应该存储在哪个分片上。
- 数据查询时,分片控制:根据查询条件,确定需要查询哪些分片,然后并发查询这些分片,最后合并结果。
- 数据新增流程:客户端请求任意一个协调节点,协调界面将请求发送到指定的分片节点,分片节点保存后,副本进行保存,然后返回客户端
- 数据查询流程:客户端请求任意一个协调节点,协调节点根据查询条件,确定需要查询哪些分片,然后并发查询这些分片,如果分片同时存在主分片和副本分片,则协调节点会随机选择一个分片进行查询,然后合并结果返回客户端。
- 数据更新流程:客户端请求任意一个协调节点,协调节点将请求发送到指定的分片节点,分片节点更新后(如果当时分片正在被使用,则重试,超过最大次数则放弃),副本进行更新,然后返回客户端。
Elasticsearch的近实时(Near Real-Time, NRT)搜索
Elasticsearch的”近实时”(Near Real-Time, NRT)搜索是其核心特性之一,指的是在文档被索引(写入)后,通常在非常短的时间内(默认为1秒)即可被搜索到。这并不是绝对的实时(即写入操作成功返回响应后立即就能查到),而是存在一个极其短暂的延迟。理解NRT的关键在于了解Elasticsearch底层的写入和刷新机制。
倒排索引与分段(Inverted Index & Segments):
- Elasticsearch的索引实际上是由许多更小的、不可变的Lucene索引(称为分段)组成的。
- 每个分段包含其建立时所有文档的倒排索引。
- 分段一旦创建,就不能再被修改(追加新文档或更新现有文档)。
写入流程:内存 -> 分段 -> 可搜索
- Step 1: 写入到In-Memory Buffer:当你索引一个新文档时,它首先被写入到一个
内存中的缓冲区(In-Memory Buffer)。此时文档还不可被搜索。 - Step 2: 写入到Transaction Log(Translog) :同时,操作会被追加写入到磁盘上的
Transaction Log(Translog)中。这是一种持久化的预写日志(Write-Ahead Log)。确保即使发生硬件故障或节点崩溃,尚未写入磁盘的数据也不会丢失,sync_interval:默认1s,index.translog.durability: "async"(如果是request,那么sync_interval不生效)。在重启时,可以通过重放translog来恢复丢失的操作。 - Step 3: Refresh - 创建新可搜索分段:默认情况下,每隔1秒(可通过
index.refresh_interval设置),Elasticsearch会执行一个refresh操作。- Refresh操作会:
- 将
In-Memory Buffer中的内容清空。 - 将这些文档构建成一个新的、内存中的Lucene分段。这个新的分段还不在物理磁盘上持久化,只是存在文件系统缓存中。
- 将这个新的内存分段打开(open)并添加到索引结构中的活跃分段列表中。
- 将
- 关键点: 一旦refresh完成,这个新创建的、内存中的分段就变得可被搜索了!这就是那”1秒”延迟的来源。新索引的文档要等到下一次refresh发生(最长1秒后)才能被搜索到。
- Refresh是一个相对轻量级的操作(主要涉及内存和文件系统缓存),但过于频繁(比如设置为
1ms)会显著增加集群开销。
- Refresh操作会:
- Step 4: Flush - 段持久化
- 为了防止translog变得过大(重放时间长、占用磁盘空间),以及确保内存中的分段数据不会在节点故障时丢失,Elasticsearch会定期(默认30min)(或当translog大小达到阈值时)执行一个flush操作。
- Flush操作会:
- 触发一次新的refresh(将当前内存buffer的内容刷新成一个新的内存段并使其可搜索)。
- 将所有当前内存中尚未持久化的分段(in-memory segments)物理地写入(fsync)到磁盘。
- 清空(truncate) translog,因为数据已经安全地写入到磁盘上了。旧的translog文件会被删除。
- Flush是开销相对较大的I/O操作(涉及磁盘写入),通常由ES后台管理,默认设置比较合理。在节点恢复时会检查是否存在需要应用的translog(比如在最近一次flush之后写入的数据),如果有则重放。
- Step 1: 写入到In-Memory Buffer:当你索引一个新文档时,它首先被写入到一个
合并(Merge)
- 随着更多的文档被索引,会创建大量的小分段。
- Elasticsearch后台运行一个segments merge进程,它会选择一些小的分段,将其合并成更大的、更高效的单一分段。
- 合并过程中删除被标记为已删除的文档(文档删除本质是写一个
.del标记,物理删除在合并时发生)。 - 合并优化索引结构、减少文件句柄消耗、提升查询效率。新合并的大分段在被写入磁盘后会替换掉旧的小分段,旧的小分段最终被删除。
- 合并是资源密集型操作(CPU, I/O),主要在后台进行。
- “近实时”(NRT)总结
- 写入返回 != 可搜: 当索引操作的响应返回成功(通常是
HTTP 200)时,表示文档已经安全地写入到translog(保证持久性),并存在于内存buffer(等待刷新)。 - 刷新触发可搜: 文档需要等待下一次
refresh操作(默认间隔1秒)将其包含在新创建的内存分段(in-memory segment)中,才能变得可搜索。 - 持久化异步: 数据物理写入磁盘(通过fsync)发生在
flush操作(自动触发,间隔比refresh长得多,比如30分钟或translog满512MB)或merge过程中。- index.translog.flush_threshold_size: “512mb”
- index.translogflush_threshold_period: “30m”
- 保障: Translog在每一步都为数据提供了故障恢复的保障。
- 可配置性:
refresh_interval可以调整:- 减小(如
100ms):牺牲一些吞吐量换取更短的搜索延迟(更”实时”)。 - 增大(如
30s或-1完全禁用):提升索引写入吞吐量(更少refresh开销),适用于能接受更大搜索延迟的场景(如日志采集)。 - 完全禁用refresh后,只能通过显式调用
POST /<index>/_refreshAPI或等待flush发生(flush内部也会触发refresh)才能使新数据可搜索。
- 减小(如
Elasticsearch选举流程:
- Elasticsearch的选举流程时ZenDiscovery模块负责的,主要包含:ping和unicast两个部分
- ping阶段:节点通过节点间相互ping来确认节点是否存活,通过节点间相互ping的响应时间来确认节点的健康状态
- 对所有可以成为master的节点(node.master: true)根据nodeId进行排序,nodeId最小的节点当选为主节点
- 如果对某个节点的投票数达到一定的值(可以成为master的节点数量/2+1),且该节点自己也选举自己,则该节点当选为master节点,否则重复选举过程
Logstash
下载完成logstash后进行配置
# 再filebeat中配置logstash为输出目标
output.logstash:
hosts: ["127.0.0.1:5044"]在logstash.yml中配置logstash的总体配置,在pipelines.yml中配置输入输出,以下给出的是示例,但是实际配置需要结合具体的格式要求进行配置。
input {
beats {
port => 5044
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["http://localhost:9200"]
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{[@metadata][version]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}Kibana
下载完成kibana后,在config目录下找到kibana.yml文件,修改如下配置:
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://localhost:9200"]
kibana.index: ".kibana"启动kibana,访问http://localhost:5601,即可看到kibana的界面。
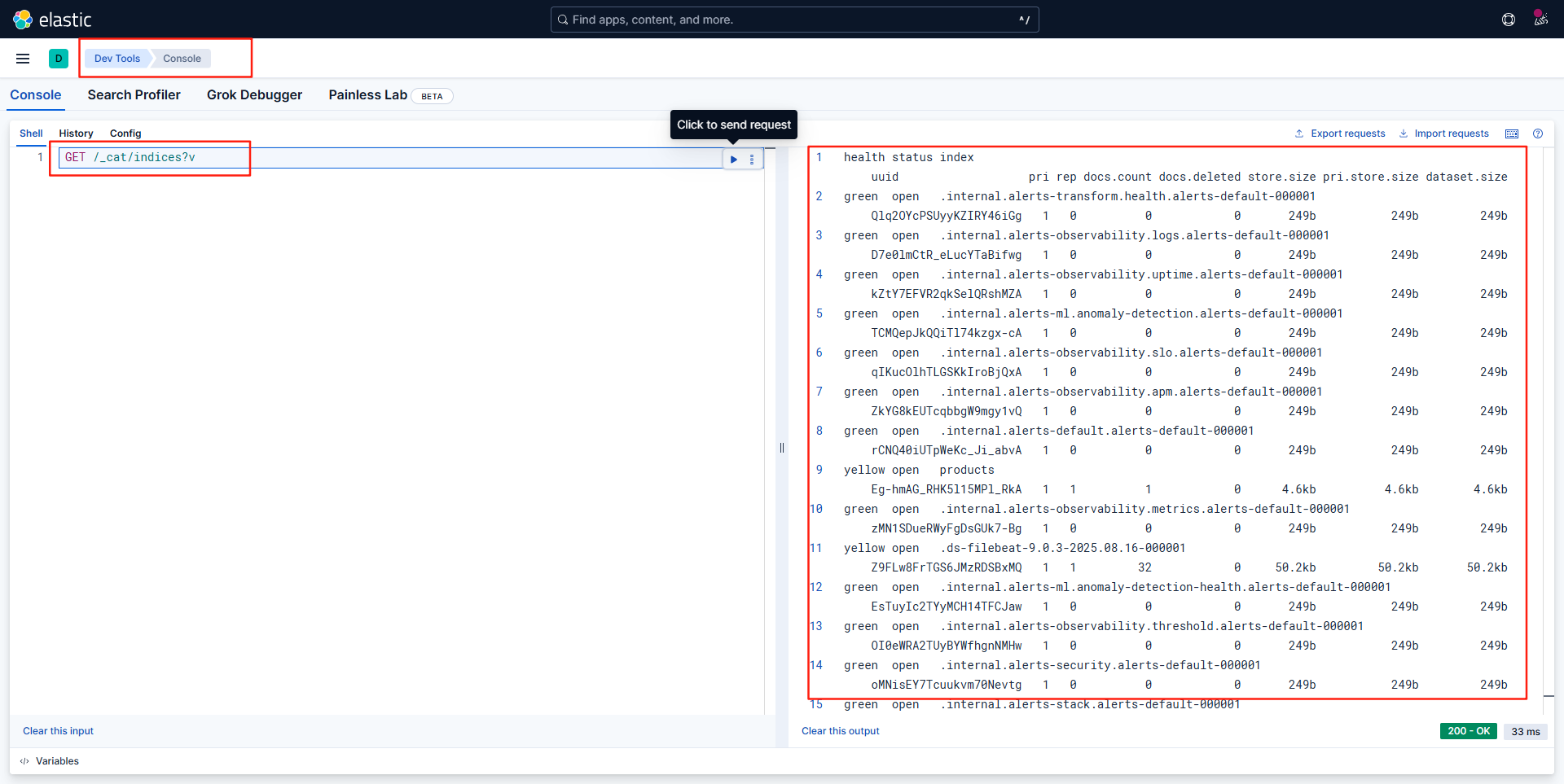
随后打开开发工具-控制台即可对elasticsearch进行搜索查询
FileBeat
下载完成filebeat之后修改yml配置文件,主要配置如下:
# Filebeat配置文件 输入配置,其中type使用filestream替换log
filebeat.inputs:
- type: filestream
# Unique ID among all inputs, an ID is required.
id: my-filestream-id
# Change to true to enable this input configuration.
enabled: true
# Paths that should be crawled and fetched. Glob based paths.
paths:
- F:/Java_work/es/log/test.log
# 配置输出到Elasticsearch
output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
# Performance preset - one of "balanced", "throughput", "scale",
# "latency", or "custom".
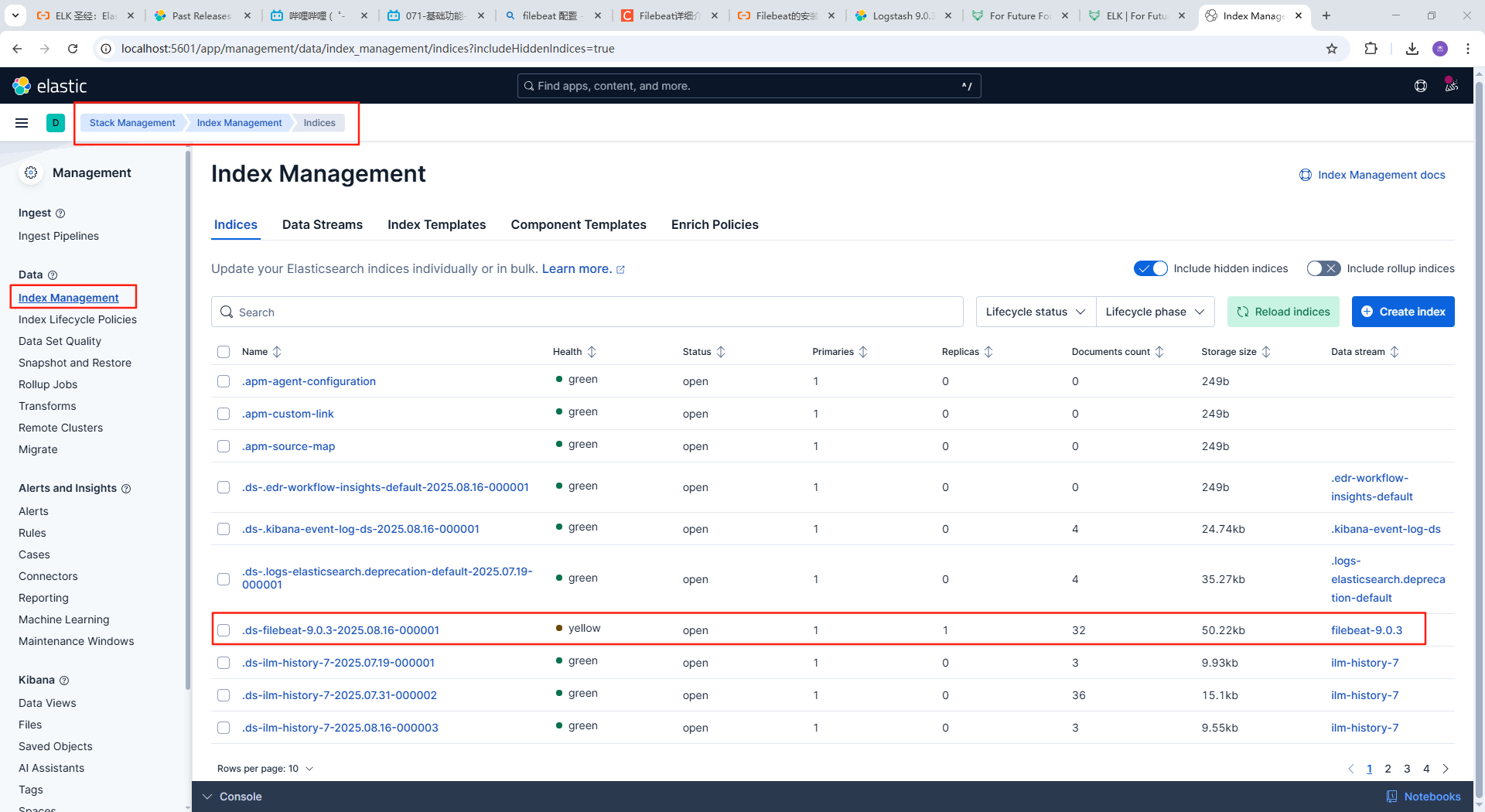
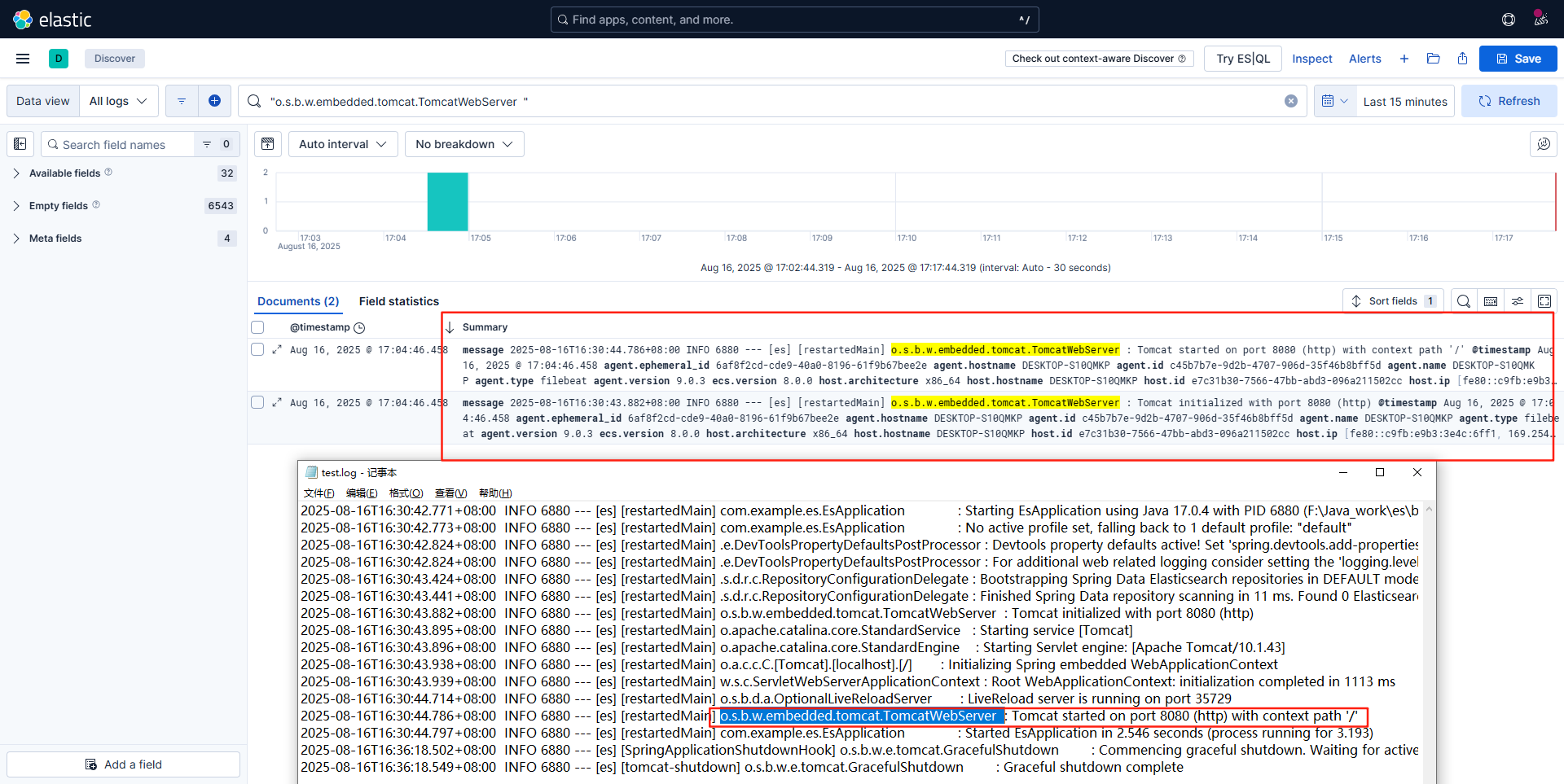
preset: balanced启动filebeat,随后可以再kibana中查看到filebeat采集的日志信息,且实时可用
filebeat.exe -c filebeat.yml -e